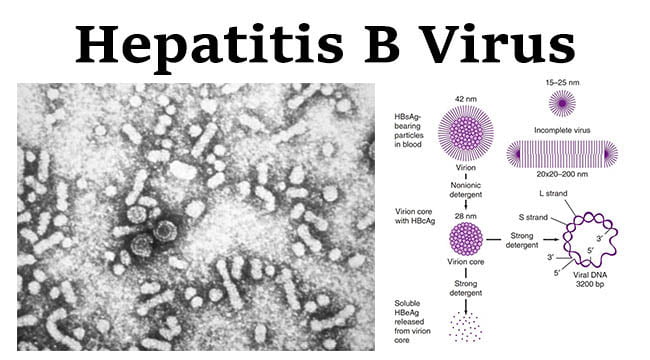
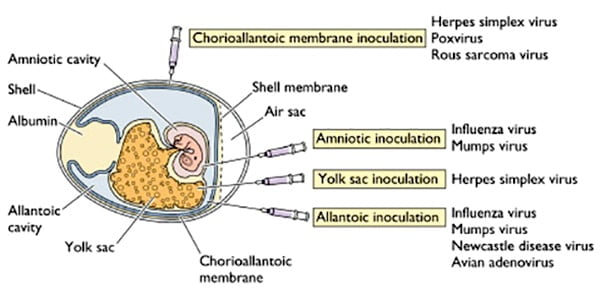
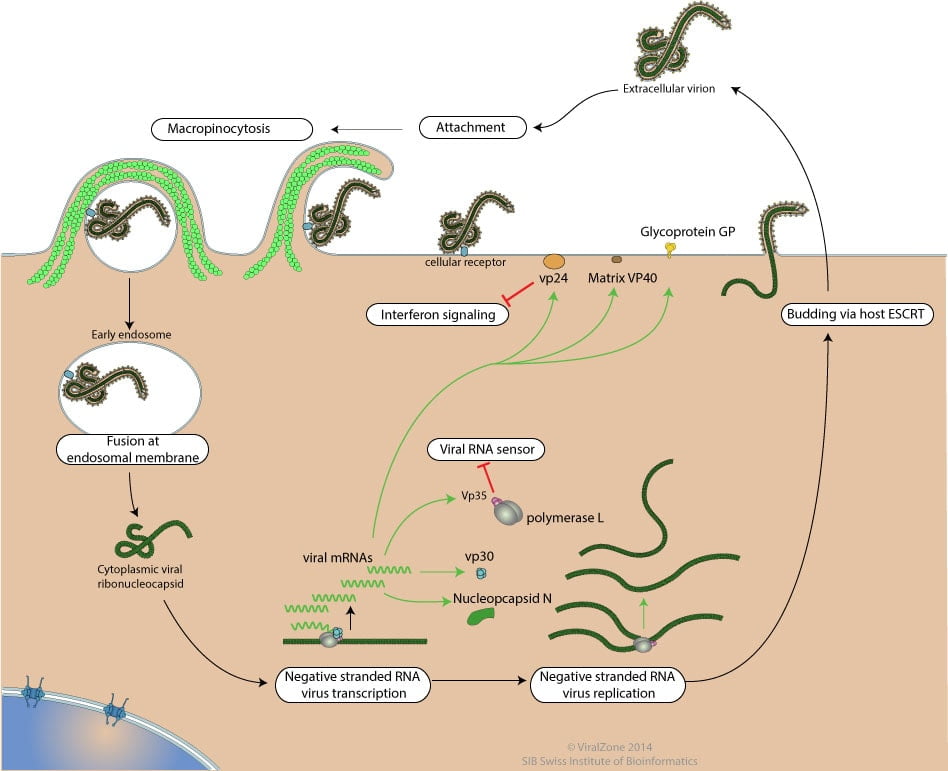
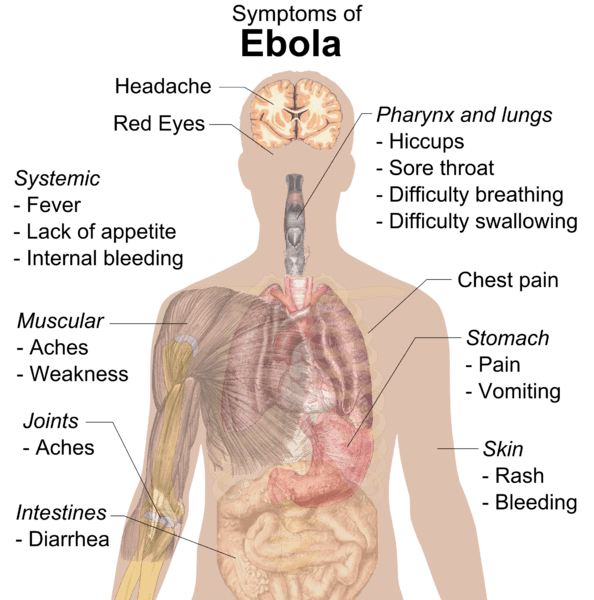
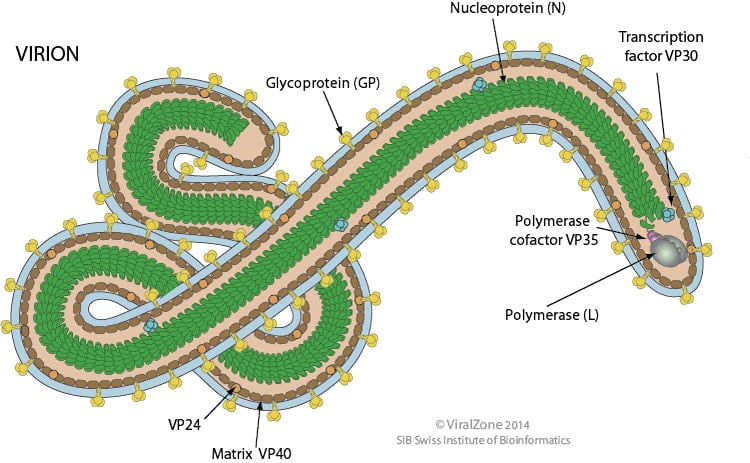
Hepatitis B Virus- Structure, Epidemiology, Symptoms, Pathogenesis, Diagnosis, Treatment and Vaccines
The hepatitis B virus is a DNA virus belonging to the Hepadnaviridae family causing hepatitis B in humans. Hepatitis B is a viral infection that attacks the liver and can cause both acute and chronic disease. Group: Group VII (dsDNA-RT)Family: HepadnaviridaeGenus: OrthohepadnavirusSpecies: Hepatitis B virus … Read more