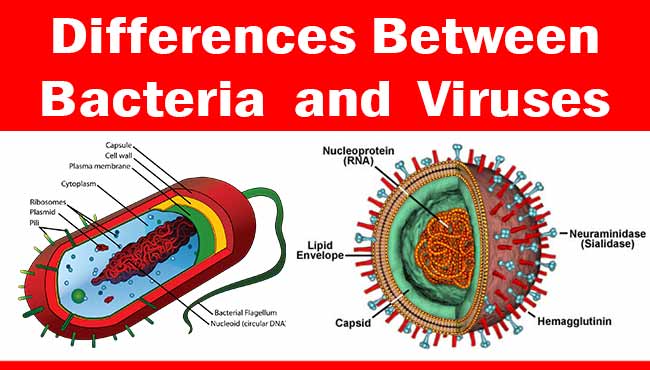
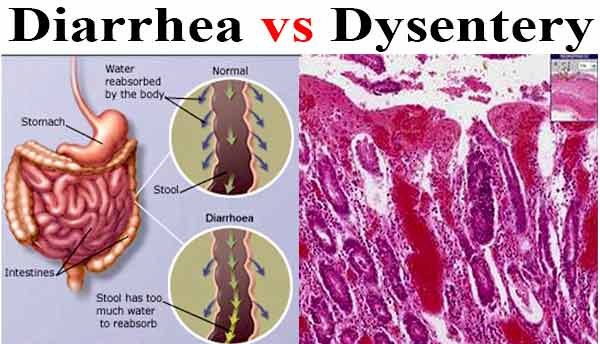
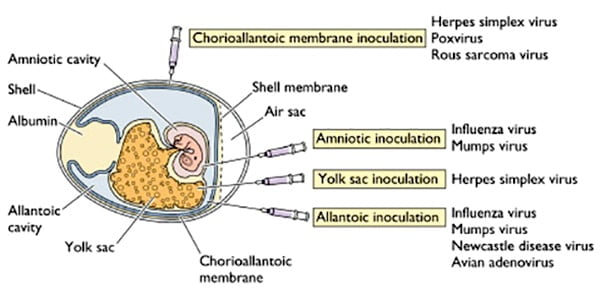
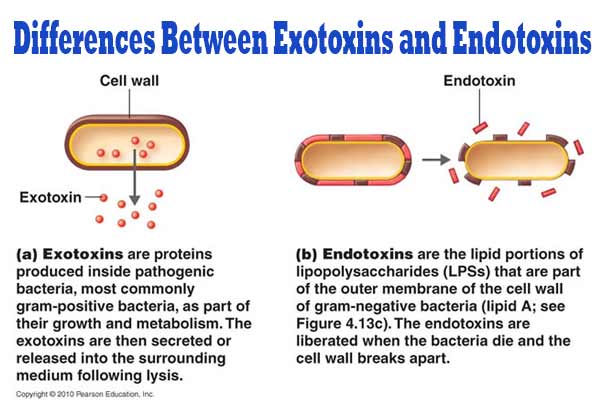
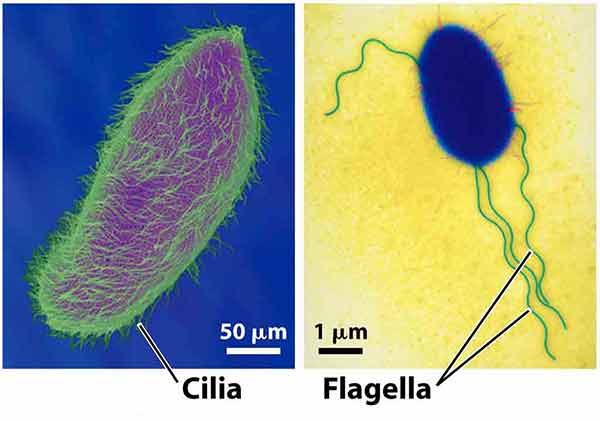
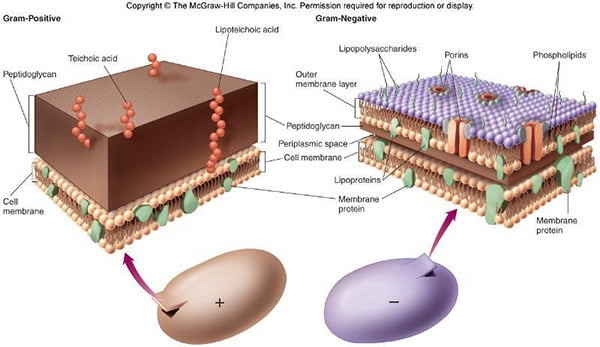
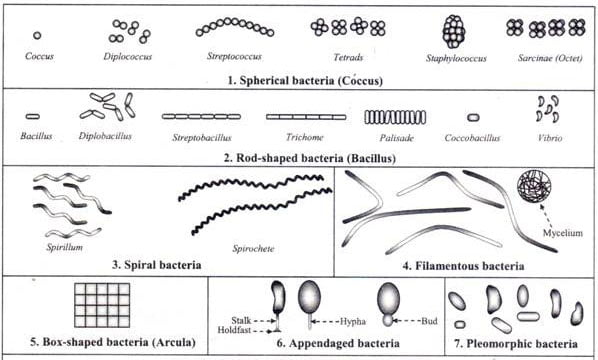
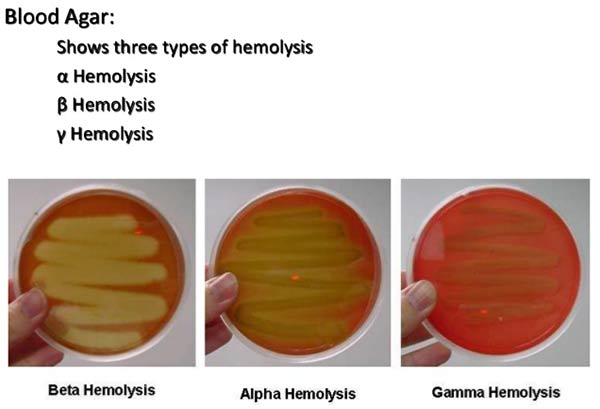
Ames Test – Introduction, Principle, Procedure, Uses and Result Interpretation
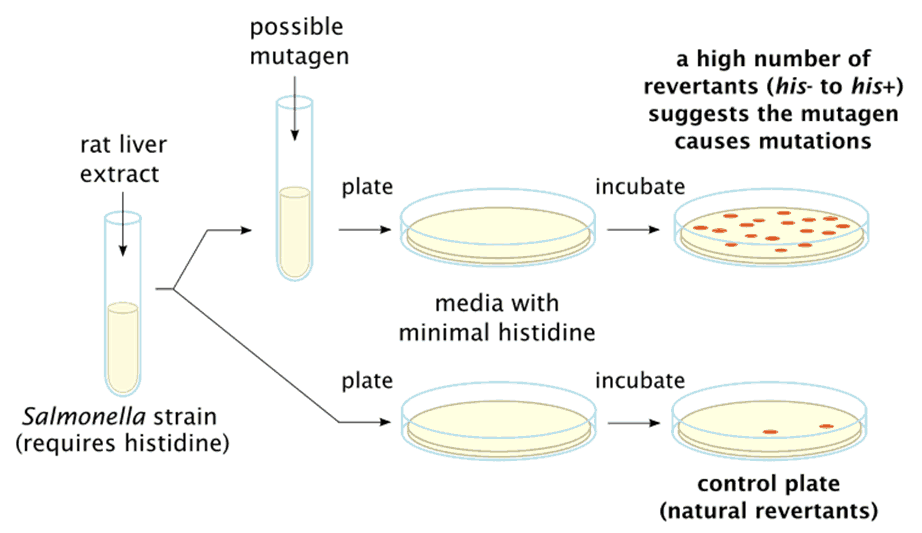
Ames test it is a biological assay to assess the mutagenic potential of chemical compounds. It utilizes bacteria to test whether a given chemical can cause mutations in the DNA of the test organism. The test was developed by Bruce N. Ames in 1970s to determine if … Read more